
Fill in the blanks by suitable conversion of units = 5 m/s so the vehicle covers 5 m in 1 s. (d) The relative density of lead is 11.3. (c) A vehicle moving with a speed of 18 km h -1 covers ………. (b) The surface area of a solid cylinder of radius 2.0 cm and height 10.0 cm is equal to …….(mm) 2. (a) The volume of a cube of side 1 cm is equal to…………m 3. NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics Physics Sample Papers

Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and Measurements : Section NameĪccuracy, precision of instruments and errors in measurementĭimensional formulae and dimensional equationsĭimensional analysis and its applications NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and Measurements Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and Measurements. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and Measurements are part of Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions.
Lakhmir Singh Science Class 8 Solutions. PS Verma and VK Agarwal Biology Class 9 Solutions. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Foundation of IT. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Foundation of Information Technology. NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Hindi Kritika. NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Hindi Kshitiz. NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Hindi Sparsh. NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Hindi Sanchayan. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Indian Economic Development.  NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science (Python). NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Psychology. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Macro Economics. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Micro Economics. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science (C++). NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science (Python).
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Computer Science (Python). NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Psychology. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Macro Economics. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Micro Economics. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science (C++). NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science (Python). #PARSEC UNIT OF MEASUREMENT PDF#
RD Sharma Class 11 Solutions Free PDF Download. All you need to know is that one parsec is roughly equal to 31 trillion km (19 trillion miles), or about 210,000 astronomical units, or 3.3 light-years. We don't need to concern ourselves with that at this stage though. However there is a good reason for astronomers to like the parsec, as it makes certain calculations based on telescope observations easier. It's also only about 3.3 times as long as the light-year, so it's used for the same kind of measurements, which almost makes it redundant. It's based on trigonometry and seems like a strange way to measure distance. Light-days = The distance a photon travels in one Earth day. Light-minutes = The distance a photon travels in one minute. Light-seconds = The distance a photon travels in one second. We can also use other units based on the travel time of light, for example: It means the distance that a photon of light can travel through the vacuum of space in one Earth year. 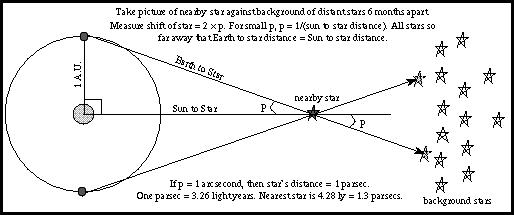
The name often confuses people-remember that a light-year is a measurement of length/distance, not time.
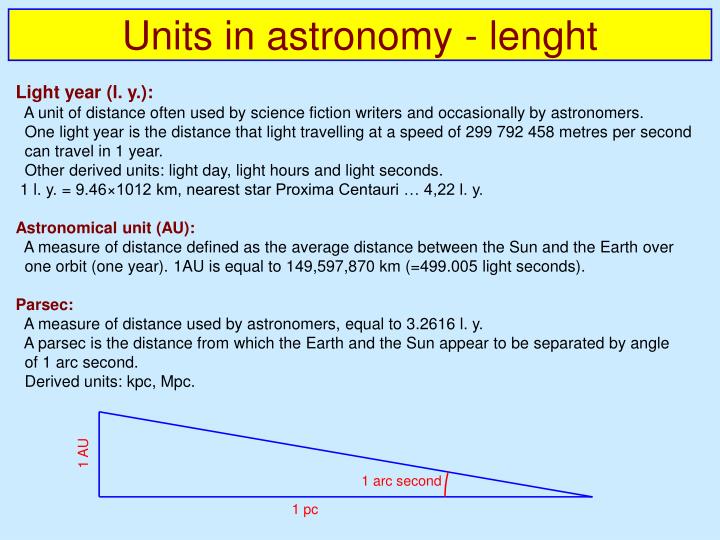
The most common measurement unit for astronomical distances is the light-year. For example, Saturn orbits the Sun at a distance of 9 au, or nine times as far away from the Sun as Earth. One AU is the average distance from the Sun to the Earth, approximately 150 million km. For everyday use, kilometres (km) are often used for distances up to the size of the Solar System, but astronomers tend to prefer to use astronomical units, light-years and parsecs. 2.5 × 10 7 m, but you don't need to worry about that if you don't want to. In academic or engineering situations, metres are often shown using scientific notation, e.g. Note: Metric is the official measurement system of astronomy. We can use kilometres or miles to measure distances within our Solar System, but the rest of the Universe requires a step up. Distances in space are so large that the measurements we use on Earth aren't often practical.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
